Seabed Sediment Measurement System (SSMS)
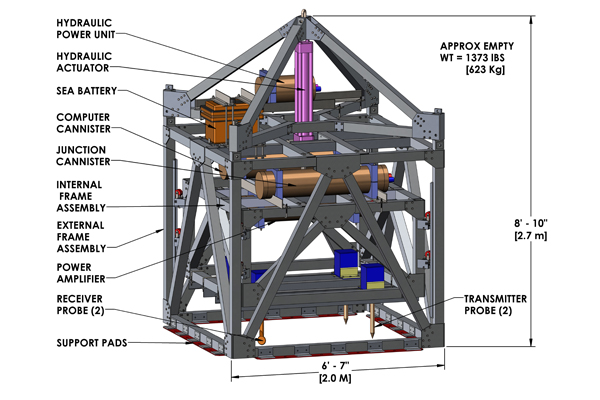
ISSAMS (In Situ Sediment Geo-Acoustic Measurement System) was originally designed for ocean floor research conducted by the Naval Research Laboratory at Stennis Space Center, MS, and was used to rapidly measure the geotechnical and geo-Acoustic properties of the ocean floor by measuring compressional and shear wave velocity and attenuation, temperature, depth, and near bottom water conductivity. Ocean floor geotechnical and geo-Acoustic properties are needed for numerous scientific and military applications. SSMS (Seabed Sediment Measurement System) is an updated version of ISSAMS but is functionally similar. Modifications include more efficient 'Inner Frame Guides', less complicated 'Lifting Frame', lighter weight, and smaller overall dimensions.
Operating Procedure
SSMS is first lowered to the ocean floor. A hydraulic cylinder is activated which lowers an inner cage and inserts shear and compression wave sensor probes into the ocean floor. After the data has been collected, the inner cage is raised which retracts the shear and compression probes. SSMS is then raised to the surface and recovered. A description of the SSMS electronic package is given in the ISSAMS report to the right.
SEABED SEDIMENT MEASUREMENT SYSTEM (SSMS)



Connect With Us